The Education Policy Hotlist
Top news in U.S. education policy for the week of October 16th - 20th
Hello, and welcome back to the Education Policy Hotlist!
I hope this email finds you well and happy this weekend. My husband has COVID-19, so I am alone managing the busy weekend schedule. Wish me luck!
In this week’s Hotlist, I have some exciting and valuable resources to share with you:
Some new resources that provide actionable AI guidance from trusted sources like TeachAI and CGCS.
A series of resources on accountability and transparency, including a 50-state legislative review from 2023 and six coalition-building strategies from the Advocacy Labs.
Lots of news about how states are getting creative to address teacher workforce challenges.
Thank you for being loyal readers and part of this community. I always appreciate your feedback and suggestions, so please get in touch with me anytime.
Cheers,
Christine
Mark Your Calendars
Tuesday, October 24th at 11:00 a.m. (PST) join a rockstar panel for a conversation about enacting change and shifts that support equity, justice, and anti-racism. Register here.
Tuesday, October 24th at 2:00 p.m. (EST), please join FutureEd for a webinar about Taking the Science of Reading to Scale. Register here.
Tuesday, October 24th at 4:00 p.m. (EST), Fordham is hosting an in-person event to discuss their recent report, Excellence Gaps by Race and Socioeconomic Status. Register here.
Tuesday, November 8th at 9 a.m., 3 p.m., and 9 p.m. (EST), Teach AI is hosting a webinar to review its new AI guidance and toolkit. Register here.
AI in Education
TeachAI: A Toolkit for AI Education
TeachAI is a non-profit organization that aims to promote AI literacy and education. The organization has created a toolkit for education authorities, school leaders, and teachers to create guidance on the responsible use of AI in primary and secondary education. The toolkit covers generative AI, predictive AI, academic integrity, privacy, security, and risk management. The toolkit also offers sample resources, such as letters, policies, and presentations, to help communicate with stakeholders and implement AI solutions in schools.
Preparing for the Future of Education with Gen AI
The Council of the Great City Schools (CGCS) and the Consortium for School Networking (CoSN) have released a new resource to help district leaders plan for the integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI) in their schools. Gen AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, images, audio, or video, based on existing data or information. The resource, called the K-12 Gen AI Readiness Checklist, provides a list of questions to consider across six core focus areas: Executive Leadership, Operations, Data, Technology, Security, and Risk Management. The checklist aims to ensure that Gen AI solutions are implemented responsibly and securely, enhancing the student, teacher, and family experience.
AI in Education: A Challenge and an Opportunity
The Thomas B. Fordham Institute invites education experts and enthusiasts to participate in their annual Wonkathon, a contest where they write essays on a specific question related to education reform. The topic for 2023 is: How can we harness the power but mitigate the risks of artificial intelligence in our schools? The participants are expected to address AI's potential benefits and challenges in education, such as personalized learning, data privacy, teacher training, and ethical implications. The submission deadline is October 31, 2023, and the best essays will be published on the Fordham Institute website.
Teacher Workforce
How to solve Alaska’s teacher shortage crisis
A new playbook developed by the Alaska Teacher Retention and Recruitment Working Group offers a comprehensive guide to help Alaska schools attract and retain qualified and diverse teachers, especially in rural and remote areas. The recommendations identify responses to the challenges that local agencies are facing in improving teacher recruitment and retention in Alaska, such as providing competitive salaries and benefits, offering incentives and support, creating a pipeline of local teachers, providing mentoring and professional development, building strong relationships, and promoting a positive culture and climate in schools. The playbook also provides practical, professional, and policy recommendations for stakeholders such as school districts, state agencies, teacher preparation programs, and legislators.
U.S. public schools face staffing shortages and technology gaps
A new National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) report reveals that most U.S. public schools face challenges hiring teachers and other personnel entering the 2023-24 academic year. The report also shows that many schools have reduced their provision of internet access and digital devices to students who need them at home compared to the previous school year. The report also highlights some community partnerships schools have established to support and engage with their local communities, especially in providing mental health care and nutrition/food assistance. The report is based on data from the School Pulse Panel (SPP), which surveys school leaders in U.S. public schools on various education-related topics. You can read about these and other data sources here.
California Considers Changing Teacher Testing System
EdSource reports that the California Commission on Teacher Credentialing is reviewing a $25.6 million contract with Pearson. This testing company provides four exams for teacher candidates: the California Basic Education Skills Test (CBEST), the California Subject Examinations for Teachers (CSET), the Reading Instruction Competence Assessment (RICA), and the California Preliminary Administrative Credential Examination (CPACE). The contract expires on Oct. 31, 2025, and the commission can rethink how the state’s teachers are tested. The article explains that some of these exams have been criticized for being a barrier for educators of color, and that some alternative options have been introduced in recent years, such as coursework or performance-based assessments.
Transparency and Accountability
The struggle and hope of parents of English learners in California
According to a recent story by EdSource, many parents of English learners are often unaware of their children’s language development progress and do not understand what their children need to do to be reclassified as fluent English proficient. This can lead to frustration, confusion, and, most importantly, missed opportunities for their children.
However, there is also hope and action. The story features the work of the Parent Organization Network, a group of advocates launching a campaign to help parents learn to monitor their children’s progress and advocate for changes in how districts communicate the information to families. The group is also working to empower parents to support their children’s learning at home and in the community. The story also gives examples of how some schools and districts are trying to improve the communication and collaboration between schools and families of English learners.
Advocacy Labs: A new report on community organizing
Marc Porter Magee released a new report that focuses on community organizing and provides advocates with a better understanding of how community organizing efforts work and how to make them work better on behalf of people-powered campaigns that put the needs of students and their families first. The report includes six concise lessons that provide a firm grounding in the field's history and practical lessons that can be used immediately.
State Legislation on Education and Workforce Data: A Review of 2023
The Data Quality Campaign (DQC) has released its annual review of state legislation that governs the collection and use of education and workforce data. The review aims to highlight key themes, promising trends, and next steps for policymakers. The review covers topics such as cross-agency data governance, statewide longitudinal data systems (SLDSs), data privacy, and data access for students and families. The review also provides examples of state legislation on education and workforce data from 2023. Key findings include:
Three states passed cross-agency data governance laws, which are essential for making robust access to data possible.
Five states and Washington, DC, funded their statewide longitudinal data systems (SLDSs) through legislation, which are critical for linking data across sectors and levels.
Seventeen states introduced 31 bills governing data privacy, and three of them passed three privacy laws, which are important for protecting data from misuse and abuse.
Two states passed laws to provide more data to students and families on their academic journeys, such as K–12 performance and postsecondary options, which are useful for making informed decisions.
Academic Achievement
Virginia's All in VA Initiative Aims to Supercharge Student Learning Through High-Dosage Tutoring
Virginia is launching "All in VA," a statewide high-dosage tutoring program as part of a $418 million academic recovery effort in response to the pandemic's impact on student learning. The program follows a research-backed model where small groups of students consistently meet the same tutor during the school day, three times a week, to help them catch up and improve academic performance. This article highlights the challenges of implementing effective tutoring programs. It emphasizes the importance of clear communication, outcome-based contracts with vendors, and considering on-site tutoring for students with profound learning gaps, providing insights into the evolving landscape of education recovery efforts.
How Some States Beat the Pandemic Learning Loss with the Science of Reading
The 74 reports on how some states have improved their students’ reading and math performance despite the pandemic and how they have adopted policies and practices based on the science of reading. The science of reading is a term that refers to the research-based knowledge of how children learn to read and how to teach them effectively. Four states have shown remarkable progress: South Carolina, Iowa, Mississippi, and Tennessee, based on data from Brown University’s COVID-19 School Data Hub, which tracks student achievement nationwide. The article also provides examples of how these states have implemented the science of reading in their schools, such as providing training and coaching for teachers, using new curricula and assessments, and offering in-person learning options for families.
Virtual Tutoring Program Boosts Literacy Skills for Young Readers, Study Finds
According to new research released Wednesday, the 74 reports on how young children learning to read made significant progress after participating in a high-dosage virtual tutoring program. The program, called OnYourMark, is targeted to students who especially struggled to learn remotely during the pandemic, and the study was conducted by experts who typically advocate for in-person tutoring. The study found that over 1,000 K-2 students in the program scored higher on literacy tests than students without the extra support. The program works by providing students with 30-minute sessions of one-on-one or small-group tutoring four times a week, using a curriculum that focuses on phonics, fluency, and comprehension. The tutors are trained and paid college students or recent graduates who use an online platform to deliver the instruction.
The Pandemic’s Lifetime Tax on Students and the Economy
Education Next reports on the impact of the pandemic on students’ learning and earnings based on data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). The article argues that the cohort of students in school in March 2020 has suffered significant learning losses, especially in math and reading, and will translate into lower lifetime earnings for them. The article estimates that the average student in this cohort will face a 6 percent income tax surcharge throughout their working lives and that the U.S. economy will grow slower in the long run due to the lower skills of the population. The article also suggests possible solutions to mitigate the effects of the pandemic, such as extending the school year, increasing teacher quality, and investing in early childhood education.
Childcare
ED Awards Grants to Support Campus-Based Child Care for Student Parents
The U.S. Department of Education (ED) has announced more than $13 million in grants to 34 higher education institutions to support or establish high-quality, campus-based childcare programs for low-income student parents. The grants are part of the Child Care Access Means Parents in School (CCAMPIS) program, which aims to help student parents complete their postsecondary education by providing them with affordable and convenient childcare options. ED also encouraged applicants to propose ways to improve the quality of their childcare services, such as increasing the compensation and support for early childhood teachers.
New Jersey Expands Free Preschool with Federal Funds
The New Jersey Monitor reports that the state will spend $25 million to expand free full-day preschool to more than 2,000 children in 19 districts by January 2023. The funding is part of the $3.7 billion American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) that the state received from the federal government to help recover from the pandemic. Preschool expansion is a priority for Governor Phil Murphy, who has pledged to make universal preschool a reality for all 3- and 4-year-olds in New Jersey.
Assessment Reform
Survey Reveals Shifting Trends in Educational Assessment Practices in 2023
In a recent survey conducted in April 2023, educators and administrators indicated that formative assessments, which monitor student learning, are the most commonly used approach in education. Summative assessments, which evaluate student learning against set standards, were the second most frequently employed. The survey also found decreased teacher-created formative assessments, suggesting a trend toward more standardized assessment practices. Despite concerns about summative assessment causing anxiety, many educators expressed positive views about this format, recommending that schools address assessment anxiety and focus on enhancing assessment skills. The report also highlights the need for assessment and accountability reform to promote innovative practices prioritizing student growth and higher-order thinking over standardized testing.
Student Well-Being
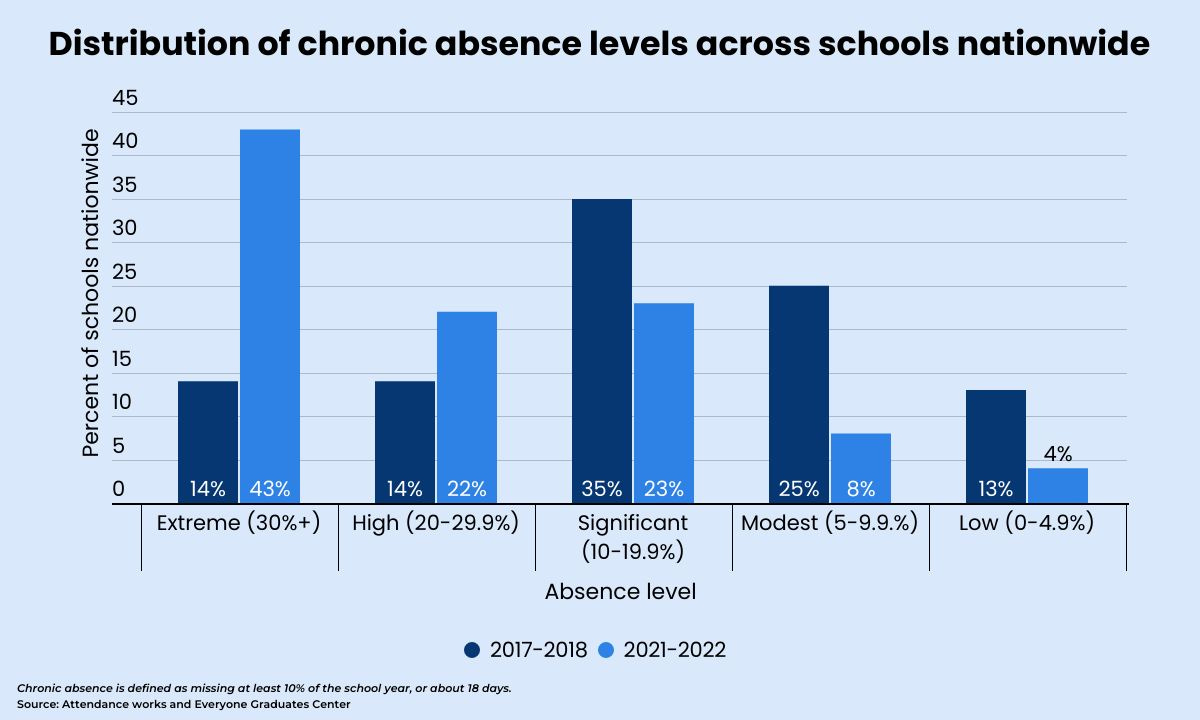
The pandemic worsened chronic absenteeism in U.S. schools
While this headline isn’t new, a recent analysis from Attendance Works and the Everyone Graduates Center at Johns Hopkins University reveals that two out of three students were enrolled in schools with high or extreme rates of chronic absenteeism during the 2021-22 school year, which is more than double the rate in 2017-18.
The analysis, which puts a fine point on what many educators know in their gut, also shows that the percentage of schools with extreme chronic absence rates, where at least 30% are chronically absent, tripled during the pandemic. The analysis suggests some of the reasons and consequences of the high levels of chronic absenteeism, such as the stressful impacts of the coronavirus outbreak and the economic recession on students and families, especially those from low-income and marginalized communities.
Education Finance
A Guide for Improving State Education Funding Systems
Bellwether Education Partners has released a publication called Lasting Change: A Policy Playbook for Improving State K-12 Finance Systems. It guides state policymakers and advocates who want to reform their state’s education funding system. The publication offers six principles for designing and implementing effective state finance systems, such as aligning funding with student needs, providing flexibility and autonomy for local decision-makers, ensuring transparency and accountability for outcomes, supporting innovation and continuous improvement, balancing adequacy and efficiency, and engaging stakeholders and building political will. The publication also provides examples of state policies and practices that illustrate these principles and recommendations for overcoming common challenges and barriers.
ICYMI
ED Seeks Input on New Program for Education Innovation
The U.S. Department of Education (ED) has published a request for information (RFI) on a potential new program, From Seedlings to Scale (S2S). The RFI seeks insight from the public to guide the efforts of the National Center for Education Research (NCER), a center within the Institute of Education Sciences (IES), to fund quick-turnaround high-reward, scalable solutions intended to improve student education outcomes. The RFI asks for responses to six questions related to the goals, design, implementation, and evaluation of the potential new program. The RFI also provides some background information on the current challenges and opportunities in education research and innovation and the existing programs and initiatives of IES. The deadline for submitting comments to the RFI is November 13, 2023.
Dr. Christine Pitts is an executive leader advancing evidence-based public policy for social impact. Follow her on LinkedIn and Instagram for more updates.







Great resource Christine. Thanks for all of the updates from around the world of K-12 education!